ตัวอย่างการใช้งานตัวดำเนินการและนิพจน์
ตัวอย่างการใช้งานตัวดำเนินการและนิพจน์ใน MQL4
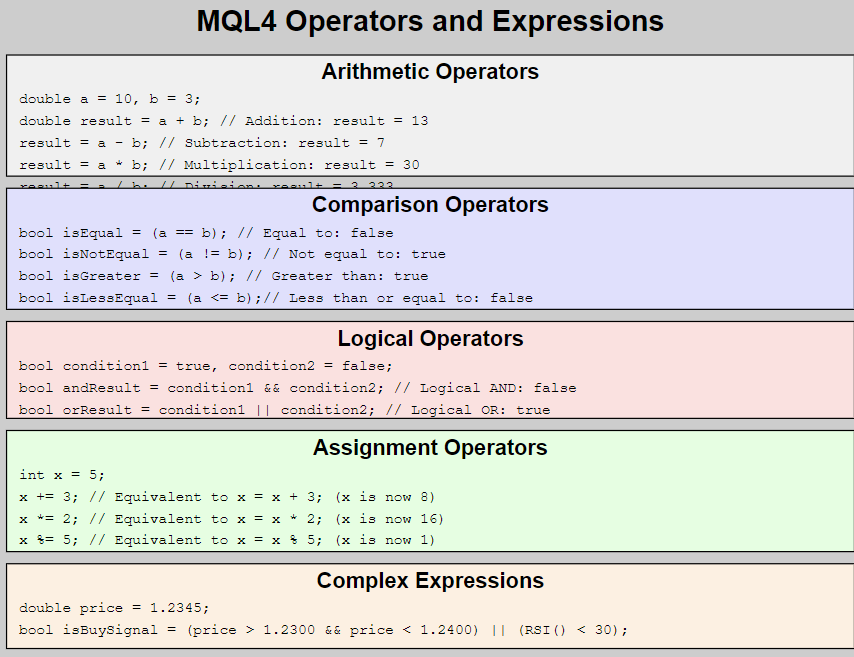
ตัวดำเนินการ (Operators) และนิพจน์ (Expressions) เป็นส่วนสำคัญในการเขียนโปรแกรม MQL4 ที่ช่วยให้เราสามารถคำนวณ เปรียบเทียบ และตัดสินใจได้ ลองมาดูตัวอย่างการใช้งานกัน:
1. ตัวดำเนินการทางคณิตศาสตร์
ใช้สำหรับการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์พื้นฐาน
double a = 10;
double b = 3;
double sum = a + b; // บวก
double difference = a - b; // ลบ
double product = a * b; // คูณ
double quotient = a / b; // หาร
double remainder = MathMod(a, b); // หารเอาเศษ
Print("Sum: ", sum);
Print("Difference: ", difference);
Print("Product: ", product);
Print("Quotient: ", quotient);
Print("Remainder: ", remainder);
2. ตัวดำเนินการเพิ่มค่าและลดค่า
ใช้สำหรับเพิ่มหรือลดค่าทีละหนึ่ง
int count = 0;
count++; // เพิ่มค่าทีละ 1
Print("After increment: ", count);
count--; // ลดค่าทีละ 1
Print("After decrement: ", count);
3. ตัวดำเนินการเปรียบเทียบ
ใช้สำหรับเปรียบเทียบค่า ผลลัพธ์จะเป็น true หรือ false
double currentPrice = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_BID);
double movingAverage = iMA(Symbol(), 0, 20, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0);
bool isAboveMA = currentPrice > movingAverage;
bool isBelowMA = currentPrice < movingAverage;
bool isEqualMA = currentPrice == movingAverage;
Print("Price is above MA: ", isAboveMA);
Print("Price is below MA: ", isBelowMA);
Print("Price is equal to MA: ", isEqualMA);
4. ตัวดำเนินการทางตรรกศาสตร์
ใช้สำหรับรวมเงื่อนไขหลายๆ อัน
bool isTrendUp = true;
bool isVolumeLow = false;
bool shouldBuy = isTrendUp && !isVolumeLow; // AND
bool shouldSell = !isTrendUp || isVolumeLow; // OR
Print("Should buy: ", shouldBuy);
Print("Should sell: ", shouldSell);
5. ตัวดำเนินการกำหนดค่า
ใช้สำหรับกำหนดค่าให้กับตัวแปร
double takeProfit = 0;
takeProfit = 50 * Point; // กำหนดค่าปกติ
takeProfit += 10 * Point; // เพิ่มค่า
Print("Take Profit: ", takeProfit);
takeProfit -= 5 * Point; // ลดค่า
Print("New Take Profit: ", takeProfit);
6. ตัวดำเนินการแบบมีเงื่อนไข
ใช้สำหรับเลือกค่าตามเงื่อนไข
bool isBuySignal = true;
string tradeDirection = isBuySignal ? "Buy" : "Sell";
Print("Trade Direction: ", tradeDirection);
double stopLoss = isBuySignal ? Ask - 20*Point : Bid + 20*Point;
Print("Stop Loss: ", stopLoss);
การใช้นิพจน์ในสถานการณ์จริง
ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างการใช้ตัวดำเนินการและนิพจน์ในการสร้างเงื่อนไขการเทรด:
void CheckTradeCondition()
{
double currentPrice = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_BID);
double ma20 = iMA(Symbol(), 0, 20, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0);
double ma50 = iMA(Symbol(), 0, 50, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0);
bool isMa20AboveMa50 = ma20 > ma50;
bool isPriceAboveMa20 = currentPrice > ma20;
if(isMa20AboveMa50 && isPriceAboveMa20) {
Print("Bullish trend detected. Consider buying.");
// เพิ่มโค้ดสำหรับเปิดคำสั่งซื้อที่นี่
}
else if(!isMa20AboveMa50 && !isPriceAboveMa20) {
Print("Bearish trend detected. Consider selling.");
// เพิ่มโค้ดสำหรับเปิดคำสั่งขายที่นี่
}
else {
Print("No clear trend. Wait for better opportunity.");
}
}
ในตัวอย่างนี้ เราใช้ตัวดำเนินการเปรียบเทียบและตัวดำเนินการทางตรรกศาสตร์เพื่อสร้างเงื่อนไขการเทรดอย่างง่าย
การเข้าใจและใช้งานตัวดำเนินการและนิพจน์อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถสร้างโลจิกการเทรดที่ซับซ้อนและยืดหยุ่นได้มากขึ้น ซึ่งเป็นพื้นฐานสำคัญในการพัฒนา EA ที่มีประสิทธิภาพ

FOREXDUCK (นามปากกา) นักเขียนของเรามีประสบการณ์การเงินการลงทุนกว่า 10 ปี มีความเชี่ยวชาญในการวิเคราะห์ตลาด Forex และคริปโต โดยเฉพาะการวิเคราะห์ทางเทคนิค รวมถึงเทคนิคต่าง